If you’ve brushed your teeth in the past 70 years, chances are you’ve heard about fluoride and its role in preventing cavities. What you might not be as familiar with is nano hydroxyapatite (nHA), a safe and incredibly effective ingredient that has been growing in popularity for use in oral care.
In this guide, we’ll break down what nano hydroxyapatite is, why it’s a game-changer for your oral health, what to look for when picking an nHA toothpaste, and why it just might be a better choice for your teeth.

what is hydroxyapatite?
main component of bones and teeth
main component of bones and teeth
Hydroxyapatite (HA) makes up around 70% of human bone and 97% of tooth enamel, providing structural strength and hardness. In its purest form HA is white, which is why your bones and teeth are naturally white as well.
calcium and phosphorus based
calcium and phosphorus based
To be a bit more scientific, hydroxyapatite is a naturally occurring form of calcium phosphate with the chemical formula Ca₁₀(PO₄)₆(OH)₂, known for its crystalline structure.
biocompatibility
biocompatibility
Since it already exists in your body, hydroxyapatite is highly biocompatible. This means it can naturally integrate with human tissue, making it safe for use in medical implants and dental applications.

what is nano hydroxyapatite?
not saliva dependent
not saliva dependent
Nano hydroxyapatite does not rely on the calcium and phosphate in your saliva to work. In fact, it is primarily made up of calcium and phosphate, introducing more of those elements into your saliva on its own. This means nHA works regardless of saliva conditions.
biocompatible / biomimetic
biocompatible / biomimetic
Nano hydroxyapatite feels right at home in your mouth. Since your teeth are primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, they naturally recognize and absorb the nano particles. This allows for remineralization from the inside out leading to a stronger and brighter smile.
safe and non-toxic
safe and non-toxic
Nano hydroxyapatite poses no risk of toxicity or overexposure since it is recognized by the body. This makes it safe for all ages, even children who tend to swallow toothpaste.
supporting enamel health:
supporting enamel health:
Nano hydroxyapatite helps support and replenish the surface of your enamel, filling in microscopic areas of weakness and helping smooth the look and feel of your teeth. By restoring a healthier enamel surface, it helps enhance natural whiteness and promote overall enamel strength for a clean, refreshed mouth.
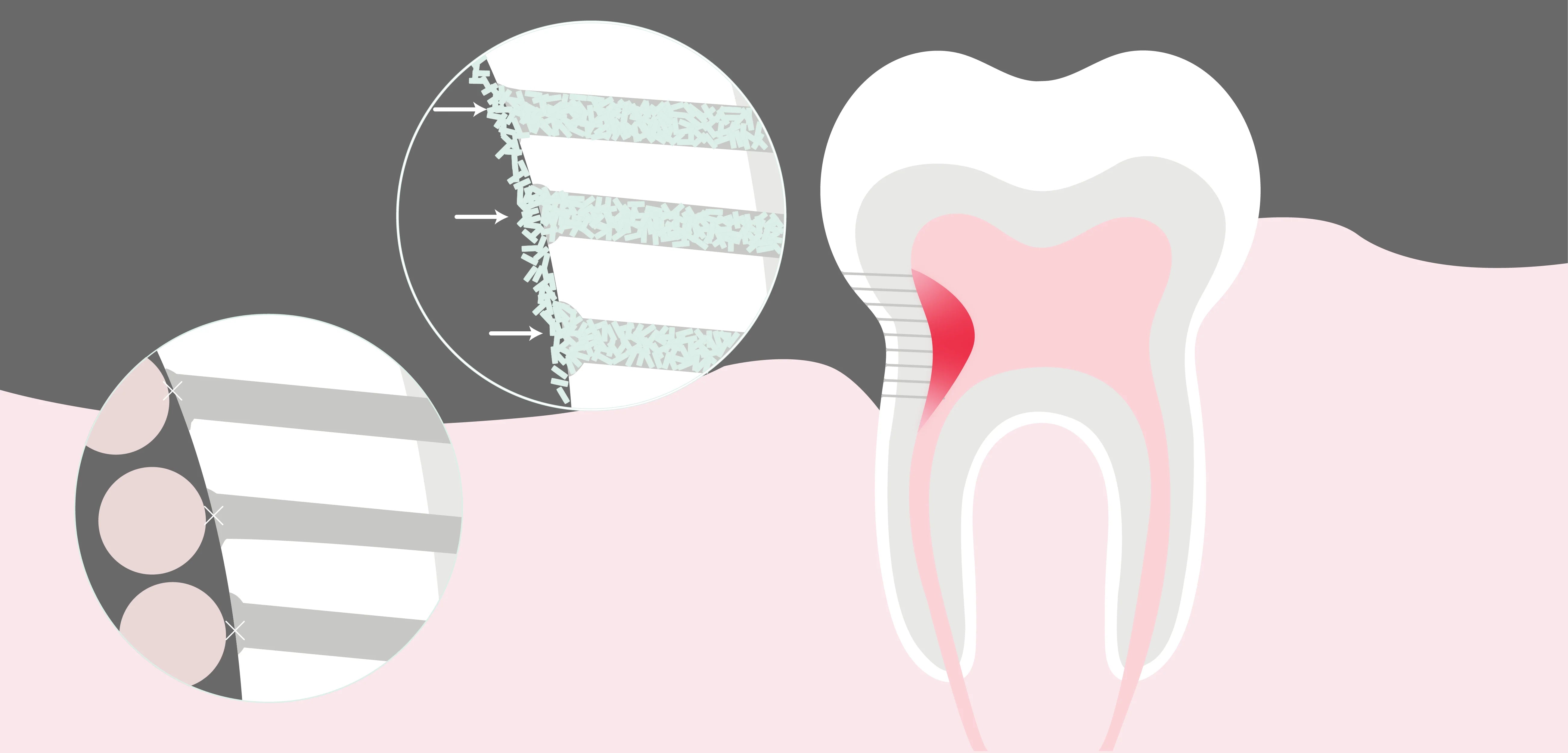
remineralization and sensitive teeth
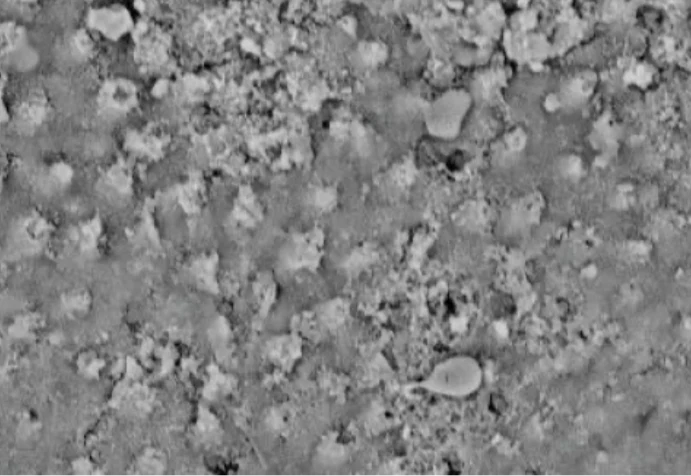
Independent third party lab tests show how exposed dentin tubules (the holes in enamel that cause sensitive teeth) are filled in and the enamel is strengthened after just 5 days of brushing with Davids nano hydroxyapatite toothpaste.


nano vs. micro hydroxyapatite
does particle size really matter?
penetration and remineralization
penetration and remineralization
Nano hydroxyapatite’s smaller particle size allows it to penetrate deep into enamel, filling in microscopic cracks and restoring minerals more effectively.
Micro hydroxyapatite, while still beneficial, primarily remains on the tooth’s surface and doesn’t reach the same depths to effectively remineralize or support sensitive teeth.
supporting sensitive teeth
supporting sensitive teeth
Nano hydroxyapatite can occlude exposed dentin tubules quicker and more thoroughly than micro particles, providing real support for sensitive teeth.
Micro hydroxyapatite provides some surface level relief but the particles are larger than the tubule opening, so it doesn’t penetrate as deeply or provide the same lasting performance.
aesthetic benefits
aesthetic benefits
Nano hydroxyapatite not only strengthens teeth but also helps smooth the enamel surface, enhancing the natural shine of your teeth.
Micro hydroxyapatite, though it offers some protection, doesn’t polish or brighten teeth to the same extent as nano particles.

not all hydroxyapatite is created equal
particle size
particle size
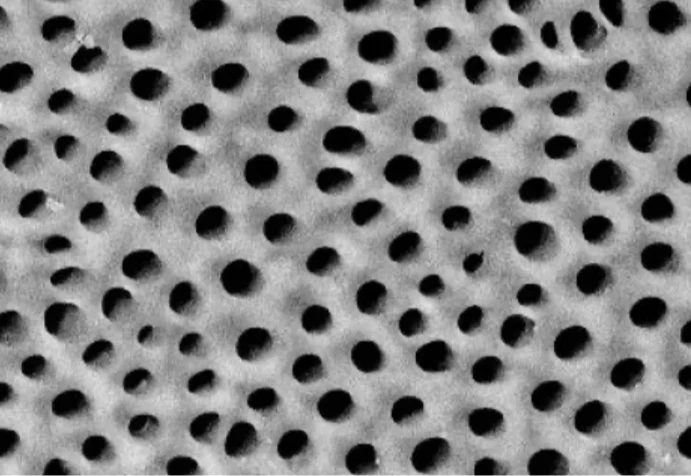
Just because a toothpaste tube says “hydroxyapatite” does not mean that it contains the same ingredients as another. Only nano sized particles (around 50 nm) are small enough to fill in the dentin tubules and microscopic fissures in your enamel. Some companies use cheaper and much larger micro hydroxyapatite, or even calcium carbonate coated in hydroxyapatite (which is 100X larger than the particle size shown to be effective).
particle shape
particle shape
There are many shapes of nano hydroxyapatite including rod, circle, needle, and irregular. However, only rod shaped
nHA is shown to be the most effective and safest. Some companies use the cheapest needle shaped particles which are banned in the EU over concerns of causing cell damage!
percentage focused marketing
percentage focused marketing
Many companies put a lot of emphasis on the percentage of hydroxyapatite in their products, but don’t talk about how well it performs. This is just a marketing ploy. Any product that focuses on percentage of hydroxyapatite should be looked at carefully, because they are likely using lower cost materials.
Davids formulates its products based on performance, not around a specific percentage of any single ingredient.